Cloves: 10 Health Benefits of Eating 2 Daily
Cloves, the unopened fragrant pink flower buds of the evergreen clove tree native to Indonesia, rank among the world’s most popular spices. Beyond their culinary appeal, these versatile buds are celebrated for their notable medicinal properties.
1. Enhancing Immune Function

Cloves stand out as an exceptional dietary choice for bolstering the immune system. They stimulate the production of white blood cells, which play a crucial role in combating infections. This immune-boosting attribute is attributed to their rich vitamin C content.
2. Promoting Digestive Well-being

3. Alleviating Toothaches
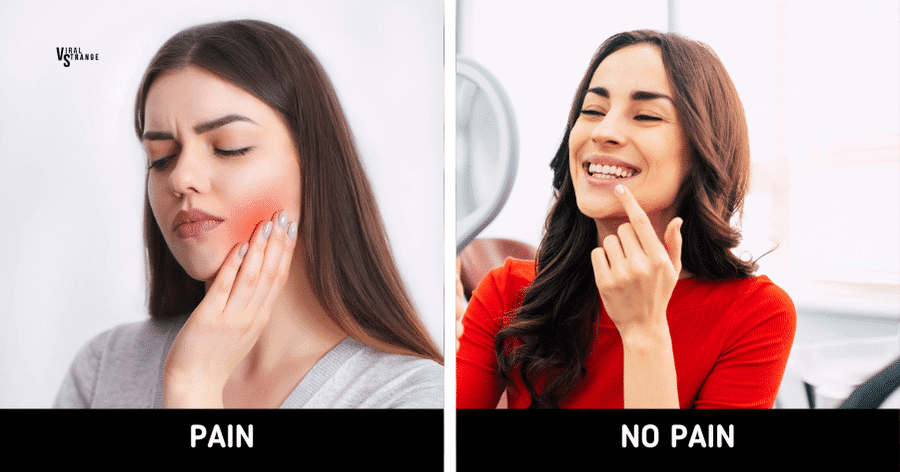

Cloves possess local anesthetic properties that make them effective in relieving toothaches. Placing a clove above the affected tooth can temporarily alleviate discomfort until dental care is sought.
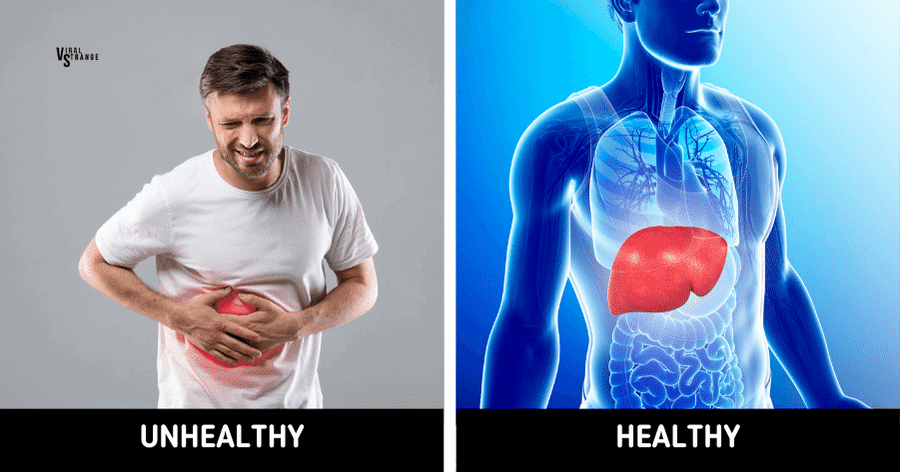
4. Supporting Liver Health
5. Reducing Pain and Inflammation

6. Beneficial for Bones and Joints
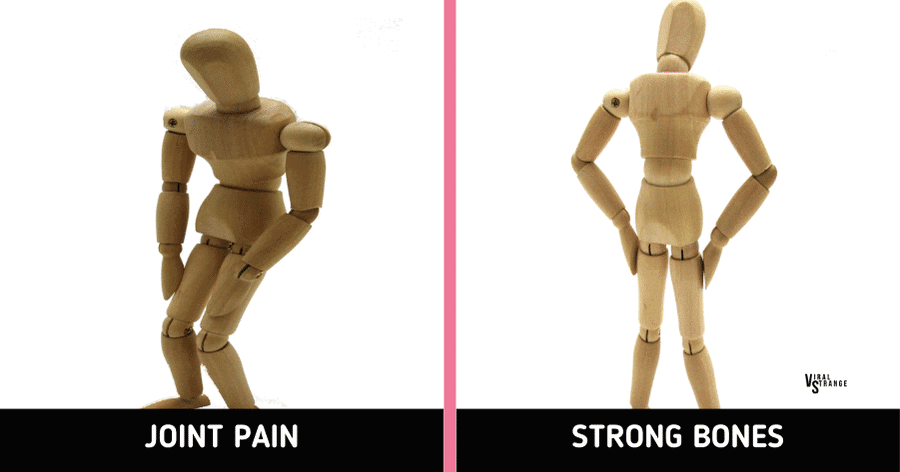
Cloves contain elements like flavonoids, manganese, and eugenol that promote bone and joint health. These substances enhance bone density, participate in bone tissue formation, and facilitate the transport of essential minerals to bones.
7. Antibacterial Properties

Research from the University of Buenos Aires revealed that clove oil effectively combats bacteria such as E. coli and Staphylococcus. A homemade herbal mouthwash made with tea tree oil, cloves, and basil can enhance gum health and reduce bacterial plaque when used for 21 days, as per the Department of Periodontics at KU Leuven University in Belgium.
8. Rich in Antioxidants
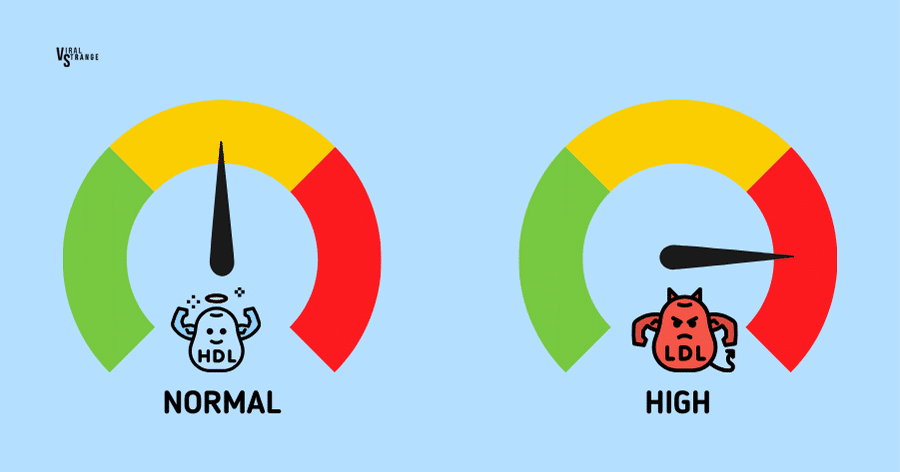
Cloves reign as the most potent dietary source of polyphenols, and micronutrients absorbed from plants. These polyphenols offer numerous health benefits, including cholesterol reduction, blood pressure control, improved artery function, and increased longevity.
9. Blood Sugar Regulation
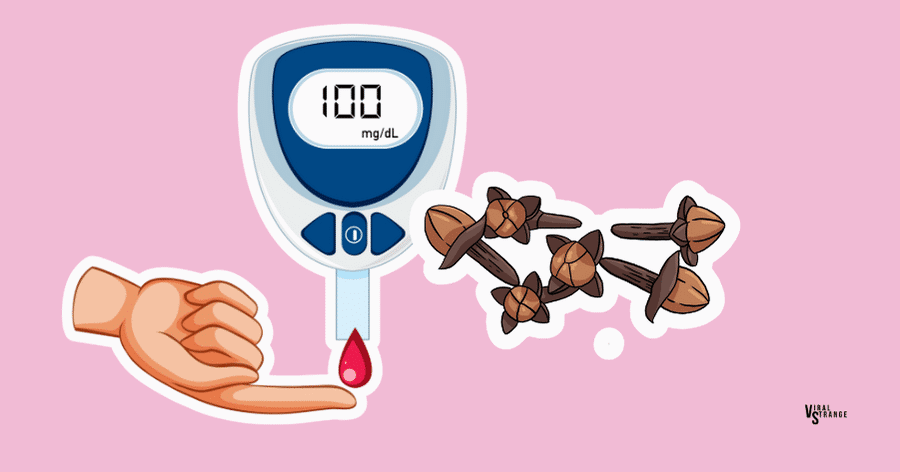
Cloves can be advantageous for individuals with blood sugar issues like diabetes, as they mimic the action of insulin. They facilitate the transfer of excess sugar from the bloodstream into cells, maintaining blood sugar balance.
10. Blood Clotting Regulation